What Is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology, or simply blockchain, is a type of distributed database renowned for its security and transparency in storing information. It originated in 2008 with the creation of Bitcoin—the first cryptocurrency—designed by an individual or group under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Initially conceived as the underlying technology for Bitcoin, blockchain enabled secure, intermediary-free transactions.
Evolution of Blockchain
Over the years, blockchain technology has evolved significantly. What began as a simple database for cryptocurrencies has transformed into a versatile tool with applications across multiple industries, including finance, logistics, healthcare, and more. This evolution has been driven by its advantages in transparency, immutability, and decentralization.
Key Components of Blockchain
Decentralization:
Unlike traditional databases managed by a central authority, a blockchain is distributed across numerous nodes in a network. This decentralization enhances its resistance to manipulation and cyberattacks.
Blocks and Chains:
The fundamental building blocks of blockchain are its blocks—collections of data. Each block is linked to the previous one through a chain, creating a continuous and tamper-evident sequence. Any alteration in one block would affect all subsequent blocks, making unauthorized changes practically impossible.
How Blockchain Works
Blockchain operates through consensus mechanisms and cryptographic security:
Cryptographic Security:
Digital signatures and cryptographic hashing safeguard data and transactions, guaranteeing the authenticity and integrity of the information stored on the blockchain.
Consensus Mechanisms:
Techniques such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) ensure that all network nodes agree on the current state of the blockchain, maintaining its integrity.
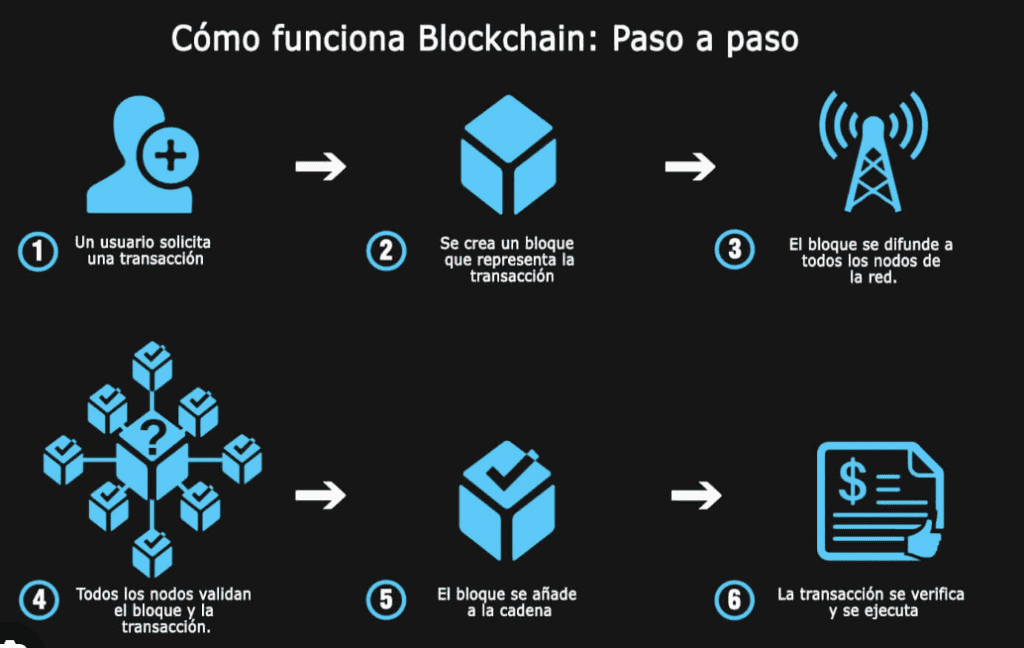
Benefits of Blockchain in International Trade
Transparency and Traceability
One of blockchain’s main advantages in international trade is its ability to offer unparalleled transparency and traceability. Because blockchain is decentralized and resistant to tampering, it allows for precise tracking of products from their origin to the final destination. This capability not only helps trading partners verify product authenticity but also significantly reduces fraud. For instance, in the food industry, blockchain enables companies to trace products “from farm to table,” enhancing trust among producers and consumers.
Cost Reduction
By eliminating intermediaries through the use of smart contracts, blockchain can considerably lower operational costs in international transactions. Companies like IBM and Maersk have demonstrated that implementing blockchain solutions can save millions of dollars annually. In one case study, Maersk reported a 20% reduction in document processing costs using its blockchain-based platform, TradeLens.
Faster Transactions
Blockchain accelerates the transaction process. Traditionally, international transactions might take days or even weeks due to multiple banking intermediaries. With blockchain, settlement can occur in minutes, thereby increasing operational efficiency and providing businesses with greater financial flexibility.
Enhanced Security and Confidentiality
Blockchain offers robust security and confidentiality. Each transaction is recorded and encrypted in a block that is added to an immutable chain, making fraudulent alterations extremely difficult. Moreover, blockchain securely handles sensitive data, protecting critical information. For example, companies like Guardtime have implemented blockchain solutions to safeguard government and healthcare data, underscoring its capability to protect highly confidential information.
Practical Applications of Blockchain in International Trade
Smart Contracts
Blockchain enables the use of smart contracts—self-executing digital agreements that automatically trigger actions when predefined conditions are met. These contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries and significantly reduce the risk of fraud. A notable application is in supply agreements, where payment is released only after products are delivered and verified by both parties.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain offers a high degree of traceability and transparency in supply chain management. Every stage of a product’s journey—from production to delivery—can be recorded on an immutable ledger. This is particularly beneficial for industries like automotive and food, where traceability is crucial for quality and safety. For instance, BMW uses blockchain technology to track the origin of materials and ensure the integrity of its supply chain.

Payments and Trade Finance
Blockchain is revolutionizing international payments by enabling near-instantaneous, low-cost transactions. It minimizes currency exchange risks and provides greater security and transparency in financial operations. Banks such as HSBC and fintech companies like Ripple are adopting blockchain to enhance their financial services, offering faster and more secure transaction options.
Challenges and Considerations
Regulation and Compliance
Adoption of blockchain in international trade faces significant regulatory challenges that vary by region. The absence of a unified global regulatory framework complicates the integration of blockchain into cross-border transactions. Different countries have divergent rules concerning cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, and data privacy, which can deter companies from adopting blockchain due to compliance uncertainties. A globally unified regulatory framework would be crucial to facilitate widespread blockchain adoption.
Adoption and Scalability
Scaling blockchain solutions to handle a high volume of transactions across global trade networks poses technical and operational challenges. Infrastructure must be robust and secure enough to process large transaction volumes. Issues like processing speed and storage capacity need to be addressed to make blockchain a viable solution at scale. Strategies such as optimizing consensus algorithms and implementing second-layer solutions (like sidechains) are key to overcoming these challenges. Successful implementations, such as Maersk and IBM’s TradeLens platform, demonstrate that with the right approach, scalability challenges can be surmounted.
Interoperability
Interoperability among different blockchain platforms is another critical challenge. With multiple platforms operating under varying standards and protocols, the lack of interoperability can hinder the seamless flow of information across networks. Initiatives like the Interledger Protocol (ILP) and the Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) aim to enable smooth transactions between different blockchain networks, which is essential for creating a cohesive and efficient global blockchain ecosystem.
Success Cases
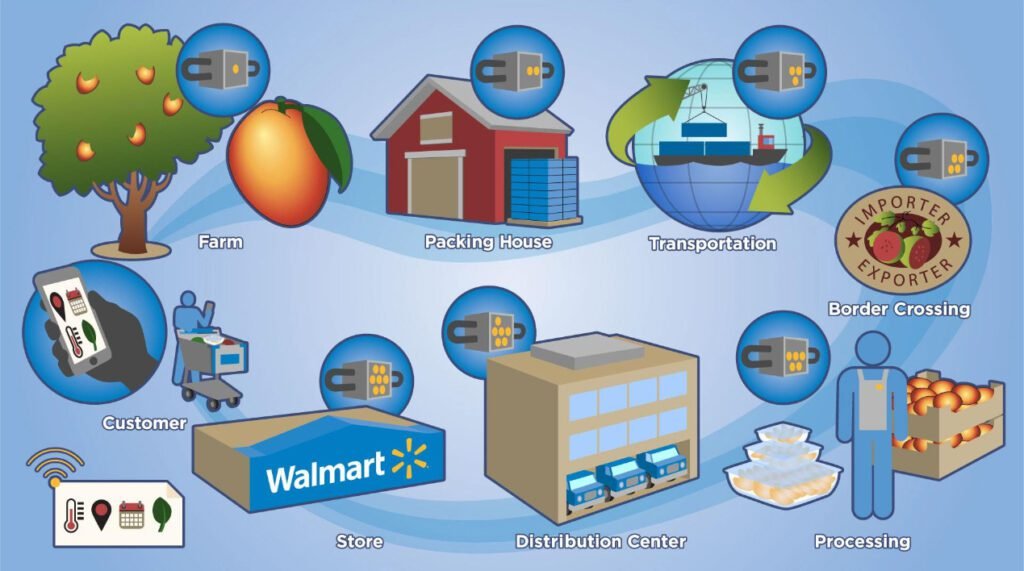
Walmart and Food Traceability
Walmart has successfully implemented blockchain solutions to enhance the traceability and safety of its food products. Given the complexity and opacity of food supply chains, quickly identifying and resolving safety issues is challenging. With blockchain, Walmart can trace the origin of food products within seconds rather than days or weeks. This instant traceability not only improves food safety but also reduces economic losses by enabling rapid responses to contamination or product recalls. Walmart’s success highlights the transformative potential of blockchain in enhancing supply chain transparency and operational efficiency.
Economic Impact of Blockchain on International Trade
The adoption of blockchain technology has the potential to significantly transform the global economy, particularly in international trade. One of the most notable impacts is the reduction of operational costs by eliminating intermediaries, making transactions more direct and less expensive. According to a Deloitte report, companies can reduce transaction costs by up to 30% by implementing blockchain-based solutions.
Additionally, blockchain improves operational efficiency. Processes that previously took days or weeks can now be completed in minutes, reducing human error and fraud risks. An IBM study revealed that using blockchain in supply chain management can improve efficiency by 15-20%, resulting in significant savings for businesses.
Blockchain also opens up new market opportunities. The enhanced traceability and transparency offered by this technology allow companies to access new markets more easily. For example, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can compete more fairly in the global marketplace, as blockchain provides a secure and transparent platform for all parties involved.
Case studies such as the one involving Maersk and IBM’s blockchain-based shipping platform demonstrate the positive impact of this technology by reducing both time and costs associated with international trade, benefiting exporters and importers alike.
Future Perspectives for Blockchain in International Trade
Blockchain has already proven to be a disruptive technology with the potential to transform international trade. Emerging trends suggest that blockchain adoption will continue to grow, driven by the need for greater transparency, security, and efficiency in global transactions.
Product Traceability
One of the most promising future applications of blockchain is enhanced product traceability. With increasing consumer demand for sustainably and ethically produced goods, companies are seeking ways to verify the authenticity and origin of their products. Blockchain allows each step of the supply chain to be recorded immutably, providing a clear and verifiable record from producer to consumer.
Innovations in Smart Contracts
Current innovations in smart contracts have the potential to revolutionize commercial agreements. These self-executing contracts, built on blockchain, can dramatically reduce the costs and time associated with intermediated transactions while minimizing fraud and human error. The automation of business processes via smart contracts could lead to greater efficiency and reliability in international trade.
Technological Convergence
Industry experts like Don Tapscott, co-founder of the Blockchain Research Institute, predict that in the coming years we will see a greater integration of blockchain with emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI). This technological convergence promises to create even smarter and more autonomous commercial systems capable of managing and optimizing supply chains in real time.
In the long term, blockchain could have a profound impact on international trade, facilitating a fairer and more transparent global trading environment. Companies that adopt this technology will be better positioned to face the challenges of global commerce and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
References:
- Nakamoto, S. (2008). Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.
- Tapscott, D., & Tapscott, A. (2016). Blockchain Revolution: How the Technology Behind Bitcoin Is Changing Money, Business, and the World. Penguin.
- Swanson, T. (2015). Consensus-as-a-service: a brief report on the emergence of permissioned, distributed ledger systems.
- IBM and Maersk (2020). TradeLens: How Blockchain is Transforming Global Trade.
- Walmart Food Traceability Initiative (2019). Using Blockchain to Ensure Food Safety.


